May 15, 2022Each kind of tRNA has a sequence of 3 unpaired nucleotides — the anticodon — which can bind, following the rules of base pairing, to the complementary triplet of nucleotides — the codon — in a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. Just as DNA replication and transcription involve base pairing of nucleotides running in opposite direction, so
Protein Synthesis (part 1): Grade 9 Understanding for IGCSE Biology 3.18B | PMG Biology
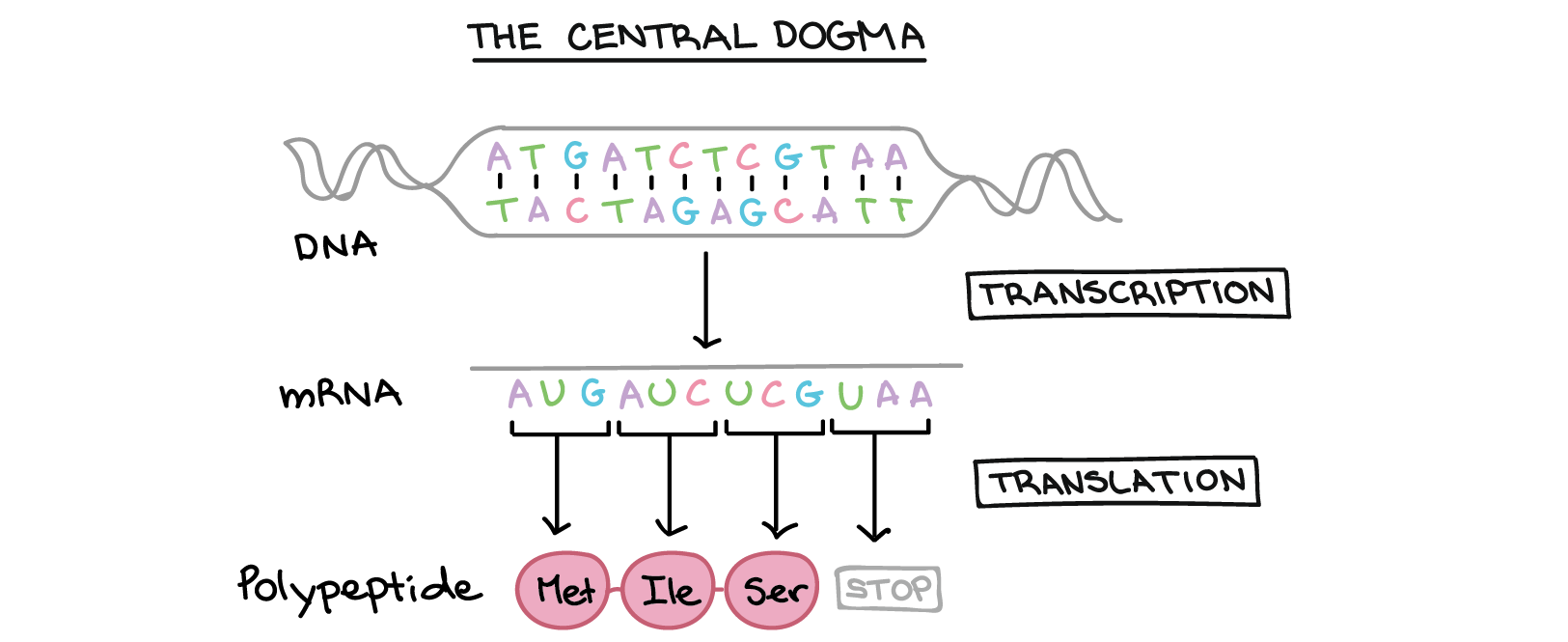
Protein synthesis is a two-step process that involves two main events called transcription and translation. In transcription, the DNA code is transcribed (copied) into mRNA. Once the mRNA is produced it moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm where it links up with ribosomes (protein making organelles) and begins churning out proteins.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Jul 30, 202217: Optional Lab Activities 17.10: Making Proteins
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
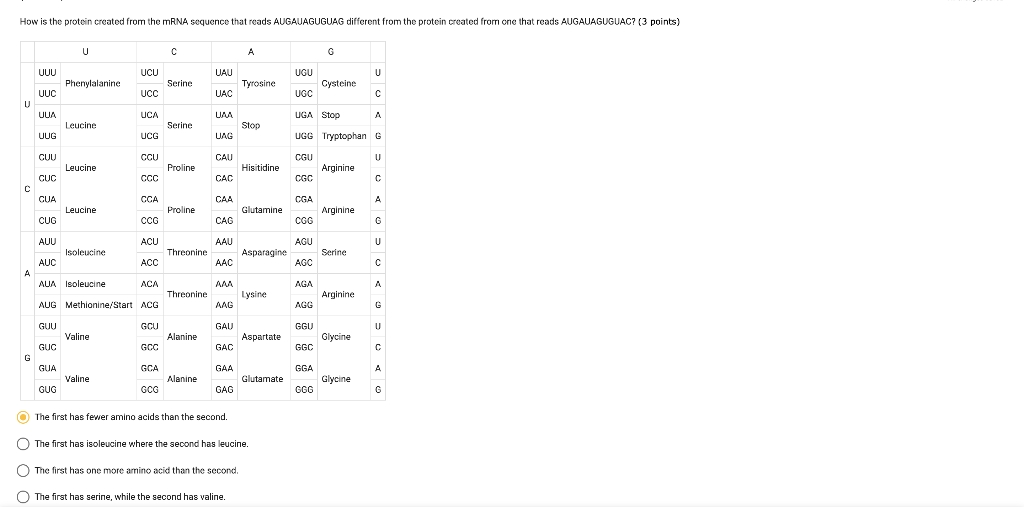
a. Determine the sequence of amino acids that will result from the translation of the segment of mRNA above. Use the genetic code in the Figure below. b. Determine the anticodon of A sequence of three nucleotides that corresponds with a specific amino acid or start/stop signal during translation: Transcription: Process during which a DNA sequence of a gene is copied to make an RNA molecule: Translation: Process during which an mRNA molecule is used to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains: Mutation: A change in a

Source Image: cellculturedish.com
Download Image
A Part Of An Mrna Molecule With The Following Sequence
A sequence of three nucleotides that corresponds with a specific amino acid or start/stop signal during translation: Transcription: Process during which a DNA sequence of a gene is copied to make an RNA molecule: Translation: Process during which an mRNA molecule is used to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains: Mutation: A change in a OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit. Give today and help us reach more students. Help Contact Us Support Center FAQ OpenStax Press Newsletter Careers Policies Accessibility Statement Terms of Use Licensing Privacy Policy
mRNA Development and Manufacturing: CMC Challenges and Solutions
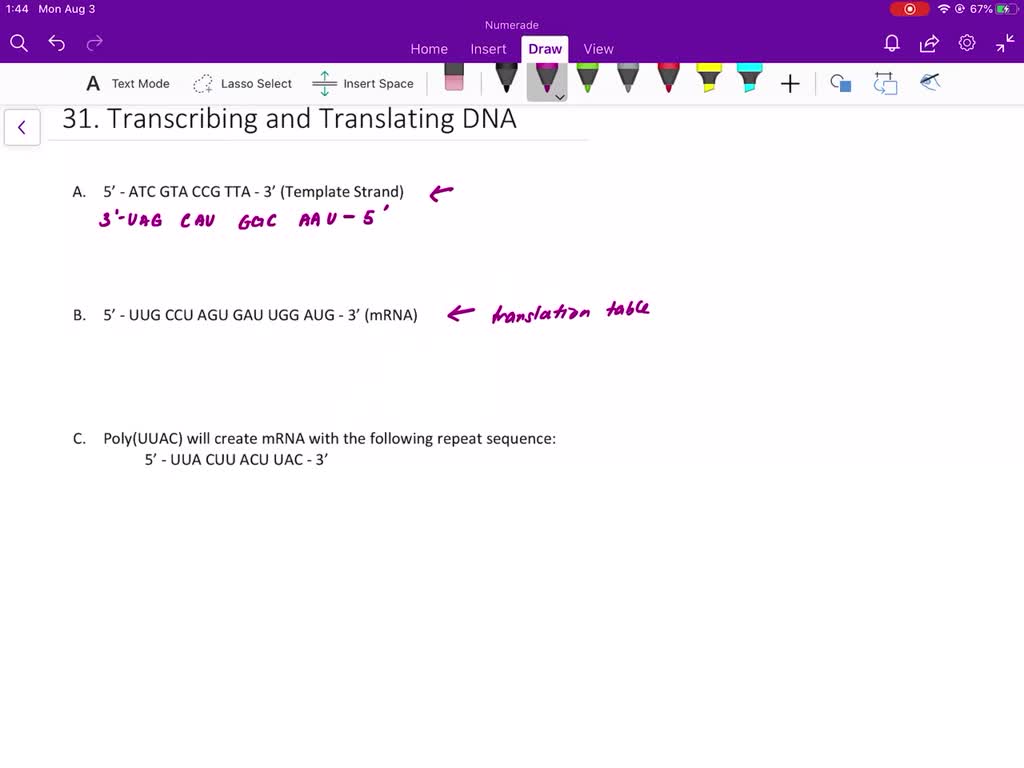
Genes encode proteins, and the instructions for making proteins are decoded in two steps: first, a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule is produced through the transcription of DNA, and next, the mRNA ⏩SOLVED:(a) Write the sequence of the mRNA molecule synthesized from… | Numerade
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
How to Use BLAST for Finding and Aligning DNA or Protein Sequences – YouTube Genes encode proteins, and the instructions for making proteins are decoded in two steps: first, a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule is produced through the transcription of DNA, and next, the mRNA

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
Protein Synthesis (part 1): Grade 9 Understanding for IGCSE Biology 3.18B | PMG Biology May 15, 2022Each kind of tRNA has a sequence of 3 unpaired nucleotides — the anticodon — which can bind, following the rules of base pairing, to the complementary triplet of nucleotides — the codon — in a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. Just as DNA replication and transcription involve base pairing of nucleotides running in opposite direction, so
Source Image: pmgbiology.com
Download Image
a. Determine the sequence of amino acids that will result from the translation of the segment of mRNA above. Use the genetic code in the Figure below. b. Determine the anticodon of Jul 30, 202217: Optional Lab Activities 17.10: Making Proteins

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
RNA Structure and Function Worksheet | Structure and function, Sequencing worksheets, Worksheets Translation. Translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology: RNA → Protein.It is the process in which the genetic code in mRNA is read, one codon at a time, to make a protein.Figure below shows how this happens. After mRNA leaves the nucleus, it moves to a ribosome, which consists of rRNA and proteins.The ribosome reads the sequence of codons in mRNA.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
3.1.8 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flashcards | Quizlet A sequence of three nucleotides that corresponds with a specific amino acid or start/stop signal during translation: Transcription: Process during which a DNA sequence of a gene is copied to make an RNA molecule: Translation: Process during which an mRNA molecule is used to assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains: Mutation: A change in a

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
A part of an mRNA molecule with the following sequence is being read by a | Course Hero OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit. Give today and help us reach more students. Help Contact Us Support Center FAQ OpenStax Press Newsletter Careers Policies Accessibility Statement Terms of Use Licensing Privacy Policy

Source Image: coursehero.com
Download Image
How to Use BLAST for Finding and Aligning DNA or Protein Sequences – YouTube
A part of an mRNA molecule with the following sequence is being read by a | Course Hero Protein synthesis is a two-step process that involves two main events called transcription and translation. In transcription, the DNA code is transcribed (copied) into mRNA. Once the mRNA is produced it moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm where it links up with ribosomes (protein making organelles) and begins churning out proteins.
a. Determine the sequence of amino acids that will result from the translation of the segment of mRNA above. Use the genetic code in the Figure below. b. Determine the anticodon of 3.1.8 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flashcards | Quizlet Translation. Translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology: RNA → Protein.It is the process in which the genetic code in mRNA is read, one codon at a time, to make a protein.Figure below shows how this happens. After mRNA leaves the nucleus, it moves to a ribosome, which consists of rRNA and proteins.The ribosome reads the sequence of codons in mRNA.